A look at some of today’s innovative uses of Facial Recognition Technology
Having looked at the broad areas where the technology is applied, let us delve into some of the interesting real-world applications, as a demonstration of how the technology is fast becoming part of our society’s fabric.
The case of Uber
Uber presents one of the most recent exciting applications through its facial recognition technology-powered ID Check. By using Microsoft’s Cognitive Services, the company has come up with what is known as Real-Time ID check which prompts drivers to capture and submit a selfie, which is used to verify the driver’s identity by comparing the image with existing ones in the database. This affords the platform a highly effective way of safeguarding against fraud and protection of driver’s accounts.
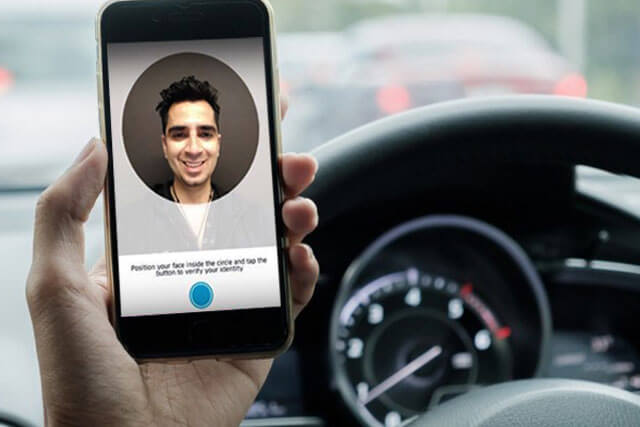

The mechanism is quite simple. Registered drivers are periodically required to capture a selfie within the app before they embark on any rides. The photo is then compared to the one on the driver’s profile through Microsoft’s cloud services. In the case of a mismatch, the account is blocked temporarily.
iPhone X’s face ID
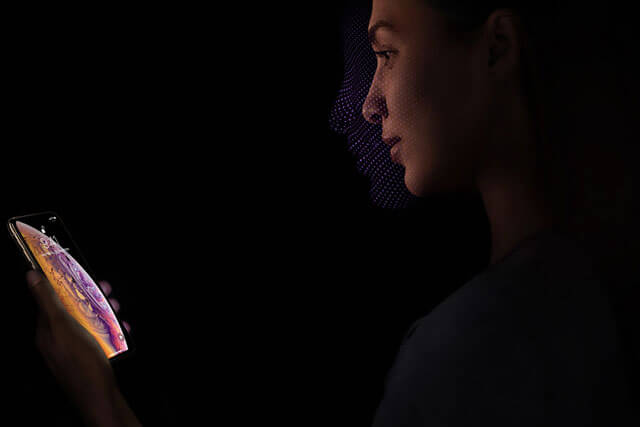

Recent times have also seen a notable number of computerized platforms and devices employ facial recognition for authentication purposes. One of the key features in the recent iPhone X from Apple is the face ID, which is a facial recognition application used to unlock the phone. Windows 10 and iPhone 4.0 are also part of the bandwagon as they incorporate facial recognition-based authentication systems.
Australian borders’ Smartgates
Facial recognition technology is at the heart of “Smartgates”, which is an automated system deployed by nine Australian International airports to accelerate the passport verification process. Any visitor with an eligible ePassport can forego the tedious manual verification process, and simply walk through two Smartgates for quick photos, present the ePassport, and let the system quickly carry out the rest of the process.
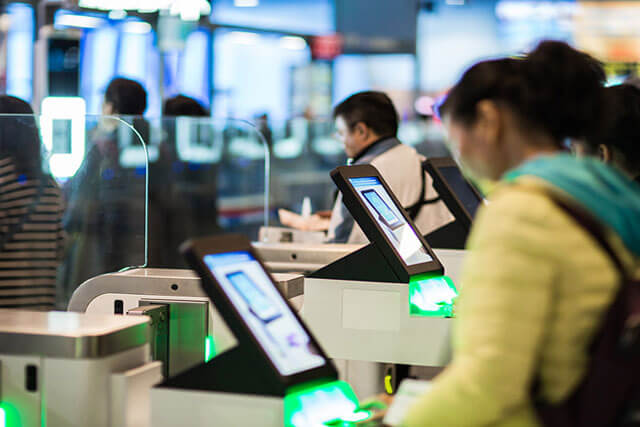

After entering the first gate, you walk through a short distance where a number of camera’s take photos from different positions. The next gate is equipped with an ePassport reader, and once you are close, it asks you to place the passport on the display face-down. After this, additional instructions, such as taking off your glasses or standing still for another photo, may be issued to further inform the verification process.
Listerine’s app for emotional detection
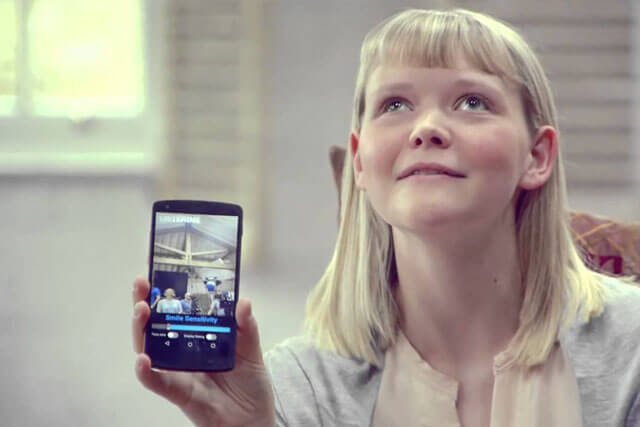

One of the most recent interesting applications goes back to 2015 when a renowned mouthwash brand known as Listerine developed an app aimed at assisting blind people to better understand the emotional atmosphere surrounding them. The mobile app is able to detect smiles within a radius of 5 meters by using facial recognition technology. Upon detection, the mobile phone beeps or vibrates to alert the user, thus fostering positive interaction.
Genetic disease diagnosis
The technology has been proven to have a remarkable success rate in the diagnosis of a number of genetic diseases which typically manifest with characteristic facial features. Classic examples include the Digeorge’s and Down’s syndrome. Although there are key facial features associated with the Digeorges syndrome, experienced clinicians often find it hard to accurately identify the condition as the features tend to manifest differently in different races and ethnic groups.
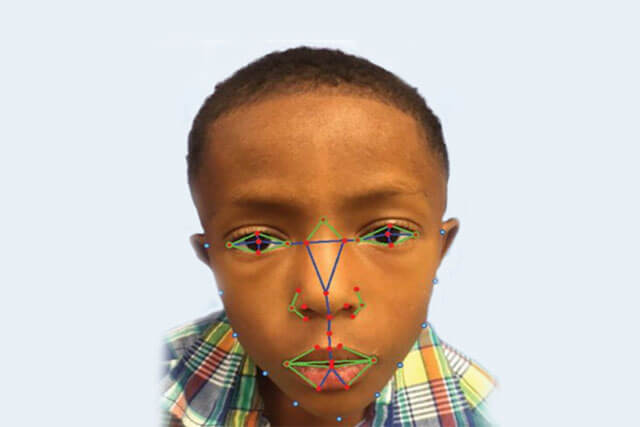
2017 sealed the technology as a step towards a timely and accurate diagnosis of the disease, as a study done by the Sheikh Zayed Institute for Pediatric Surgical Innovation at Children’s National Health System proved that the inclusion of facial analysis technology improved diagnosis success rates to 96.6%. A year earlier, the technology was also proved equally useful in the diagnosis of a more common genetic disorder which also harbours characteristic facial features, known as Down’s syndrome.
Google Photos
Google Photos features an in-built facial recognition software that groups your photos using people’s faces. While it is currently not possible to assign names to the images within the photos, the algorithm can easily identify faces and classify photos to assist you with organizing and finding specific photos quickly.
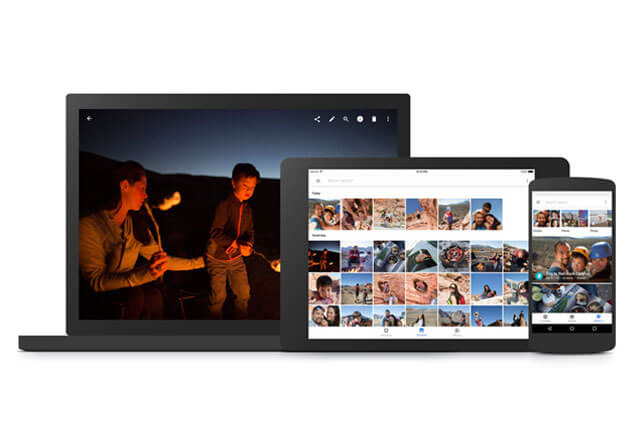
As demonstrated in the above picture, the ‘albums’ icon within the mobile app opens up several categories including ‘people’, ‘places’ and ‘things’. The ‘peoples’ category classifies photos based on available faces, while the ‘places and ‘things’ categories classify the photos based on location data if the camera is GPS enabled. However, it’s important to note that due to privacy related issues, some countries such as the U.S are not allowed access to the facial recognition capabilities of the app.
Facebook “Moments” App
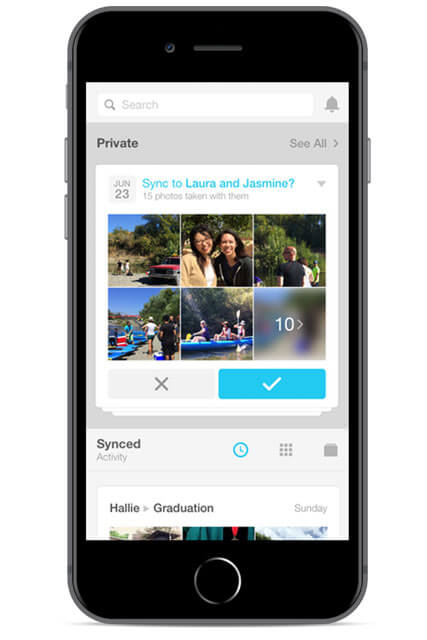
Facebook’s “Moments” app was designed to assist users with organizing and sharing their photos in a more efficient way. The app identifies which friends are in the photos, and groups them based on the identification and the time of the photoshoot. Once the classification is done, the photos can be synced with friends, who may also sync their photos as well. The synced photos are organised by the app, and specific photos can be easily found using a search feature which matches the name and faces within the photos.
Facebook holds one of the most robust databases and the prowess of its facial recognition technology is demonstrated by the fact that its first attempt in the realm of facial recognition technology known as Deepface is considered to be more accurate than FBI’s Next Generation Identification program by 12%.
Snapchat’s lenses application
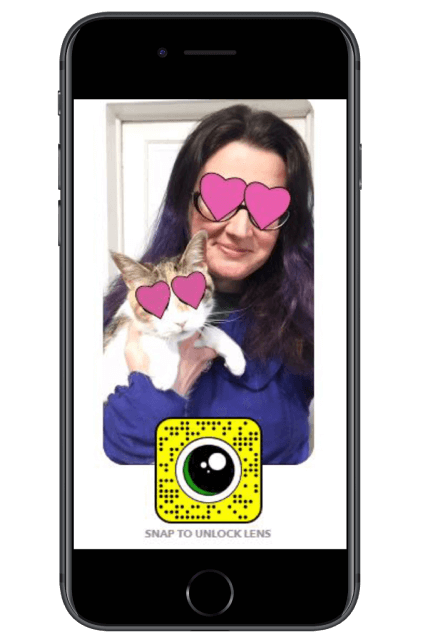
Snapchat’s “lenses”, otherwise known as “filters” or “selfie filters”, is another great example of applications of facial recognition software outside conventional applications. Formerly known as Looksery, Lenses was acquired by Snap inc in 2015. Through highly advanced facial recognition technology, the application captures and identifies faces within video or photos to allow users to modify their appearance on photos or during live streaming, such as video chats.
Like most facial recognition applications, the technology uses computer vision to detect a human face by comparing the image from the camera with a template within the system, which was built based on the key human facial landmarks from thousands of human faces. Following facial detection and identification, the system can alter and apply a variety of animations to the images according to the user’s preference.
KFC’s “smile to pay” Facial recognition system.
When you pay a visit to one of China’s 300 KFC restaurants, you’ll easily notice that the cashier’s counter queue hardly holds more than a few people. This is due to the presence of self-ordering terminals which allow people to order their food and pay with nothing more than having a photo of their face taken by the ordering system.
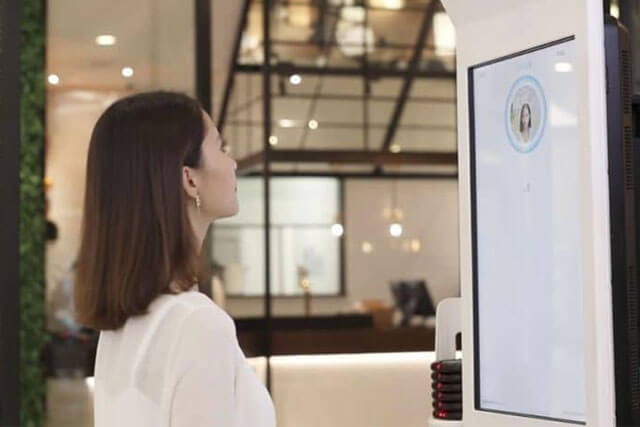

The technology was established by Ant Financial two years ago in the Chinese city of Hangzhou, which was effectively its first application in a physical store. It basically eliminates the need for any bank cards, cash or phone to carry out the transaction. Once the order is placed at the terminal, it scans the customer’s face which is then compared to the image stored in the database. A match triggers the payment transaction which is notably quicker than traditional methods.
Server-centric and device-centric architectures
Facial recognition biometric systems can be set up differently and this has implications on the suitability of a particular biometric system. A few moments of consideration of each type along with the associated advantages and disadvantages would serve us well.
On-device architecture
In this architecture, all the key steps, including storage of templates, are done on a single device. A good example is iPhone X’s facial recognition system where the captured image is compared with a template stored on the device. Here are the key up and downsides of this kind of setup.
Pros
- Unlike central servers, on-device architectures are not susceptible to large scale data breaches
- They are not vulnerable to interceptions by third parties.
- Scalable: Processing and storage of data can be done on multiple devices rather than one location.
- Faster: It eliminates the need to transfer data between the device and the server.
Cons
- The data is irretrievable once the device is damaged or stolen.
- Usage is limited to one device.
- It might not be suitable for devices with relatively low processing power.
- The data cannot be used for other matching purposes
Server-centric/Server side architecture
As suggested by the name, the matching process is carried out on a central server. In this case, after the user conducts the attempt, the image is compared to a template(s) stored on a central server.
Pros
- Data is kept secure after the device is malfunctioned or stolen.
- It saves device storage space.
- It allows access to the templates using multiple devices.
- It is an easier option for devices with low processing power.
- The data can be used for other matching purposes.
Cons
- Vulnerable to large scale attacks on servers.
- Data can be intercepted by third parties.
- Slower due to the need for data transfer.
Facial Recognition API’s
The clear benefits and immense potential associated with facial recognition systems has brought about a growing market of facial recognition products, with some of the biggest names making a decisive jump onto the bandwagon. By 2017, the market was valued at $3.87 billion, which was estimated to skyrocket to around $9.87 billion by the year 2023.
Open source facial recognition systems and a good number of commercial application program interfaces (API’s) and libraries have been gracing the market, giving developers a wide range of choices when it comes to integrating facial recognition functionality with different applications.
Google, Amazon, Microsoft, IBM, and Kairo provide some of the leading API’s on the market. However, the key to getting the best API for specific needs is knowing the advantages and limitations of different API’S and facial recognition systems. For instance, while facial recognition software for OpenCV can be exceptional with video face recognition, it doesn’t necessarily offer the same abilities on images. Let’s have a look at each of the API’s listed above in a little more detail.
Amazon Recokgnition
Rekognition is part of the Amazon Web Services (AWS) ecosystem which provides users with a robust range of tools in order to create and implement web applications. The facial recognition API allows access to Amazon’s Rekognition service, which provides a simple solution for adding video and image analysis to various applications or websites. The API was developed by the company’s computer vision scientists based on the revolutionary deep learning technology, which allows users to analyse both videos and images without prior expertise on artificial intelligence and machine learning.
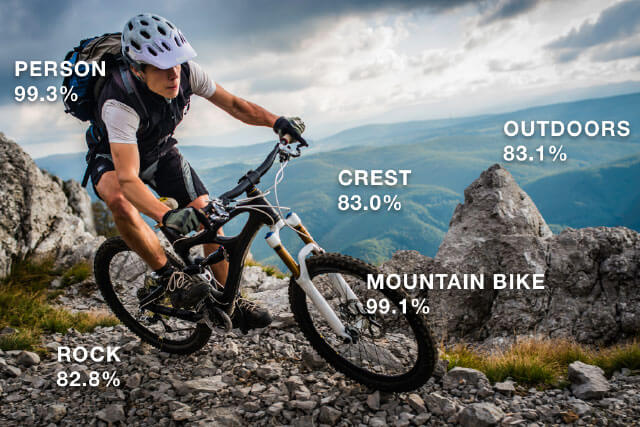
Images or video files can be stored on Amazon’s storage infrastructure known as Amazon S3 where they are accessed before being processed by the facial recognition software. To date, it offers one of the richest APIs in terms of capabilities. Let us delve a bit more into the key features.
Key features
- Facial detection
- Facial recognition (for both image and videos)
- Identification
- Emotional detection
- Age and gender identification
- Video Multi-face tracking
Limitations
Much as the API provides a commendable array of capabilities, there are a few limitations worthy of consideration.
- Lack of emotional depth identification: It does not provide an idea of the extent of a particular emotion which is commonly represented as a percentage in other API’s.
- Lack of ethnicity identification.
- It can only process 15 faces per image.
Google Cloud vision API
The Google cloud vision is part of Google’s cloud platform, which allows building, deployment, and scaling of apps, websites and other services using Google’s infrastructure. Cloud Vision provides pretrained models through the API as well as the capacity to develop customized models through the AutoML Vision application.
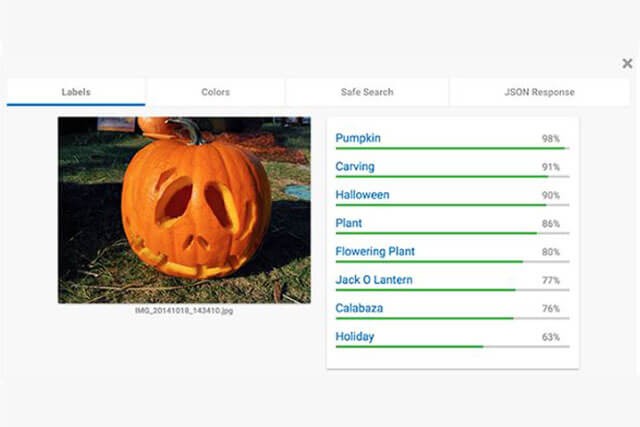
The Cloud Vision API allows users to analyse and understand the content within an image by integrating machine learning models in a user-friendly API. It has the ability to classify images into different categories, detect faces and objects, as well as identifying texts embedded in the image. Additionally, users can develop metadata on the image catalog, alter offensive and inappropriate content, and conduct emotional analysis. Here is a round-up of the key features and some of the limitations.
Key features
- Detection of offensive or inappropriate content.
- Optical character recognition: Conversion of image text into electronically encoded text.
- Automatic language identification
- Video Intelligence
Limitations
- It only uses 34 facial landmarks for detection and identification.
- The sentimental analysis only features emotional classifiers without an expression of emotional depth.
- It comes with a complex pricing system relating to the number of features you choose to incorporate in your application.
Microsoft Face API

The Microsoft face API was initially released in the year 2016 as part of Microsoft’s Cognitive Services AI cloud services. Though harbouring a few limitations, It features one of the most advanced facial recognition algorithms on the market. The key features revolve around facial detection, recognition and emotional recognition. This allows applications to detect, identify similar or identical faces, as well as identifying the associated emotion. Here is the roundup of the capabilities.
Key features
- Facial detection
- Identification
- Verification
- Emotional detection.
Limitations
- The package does not come with a software development kit (SDK) for added flexibility.
- Number of facial landmarks used is limited to 27.
- The maximum gallery size is 1000 images.
- Emotional detection does not cover depth.
- There is no ethnicity detection.
Karios

Karios is a human analytics platform allowing users to integrate facial recognition capabilities in applications through its cloud API service. The service can also be hosted on user’s servers to allow complete control of data and overall security. Through the API, Karios boasts one of the most comprehensive packages on the market by offering a wider range of facial recognition features.
Key features
- Detection
- Identification
- Verification
- Emotion Detection and depth (percentage)
- Other demographic features: Age, gender and ethnicity
- Multi-face tracking and grouping
OpenCV

OpenCV is a renowned computer vision library and platform established in 1999. The platform focuses on processing real-time images and incorporates the use of the most recent computer vision algorithms. After Willow Garage assumed support in 2008, the platform now incorporates programming interface to a number of languages including Python, C, C++, and Android. Additionally, the platform exists under a BSD licensure thus it is usable for both commercial and academic purposes.
The latest OpenCV 2.4 comes with the FaceRecognizer: a facial recognition software utilizing some advanced algorithms, which include the Eigenfaces, Fisherfaces and local binary.
Key Features
The library incorporates a number of optimized algorithms for basic and sophisticated applications.
- Face detection: Both 2D and 3D
- Video facial identification and Recognition
- Image and multi-face tracking
Limitations
- It is hard to use for those with no prior programming experience.
- It exists as SDK only
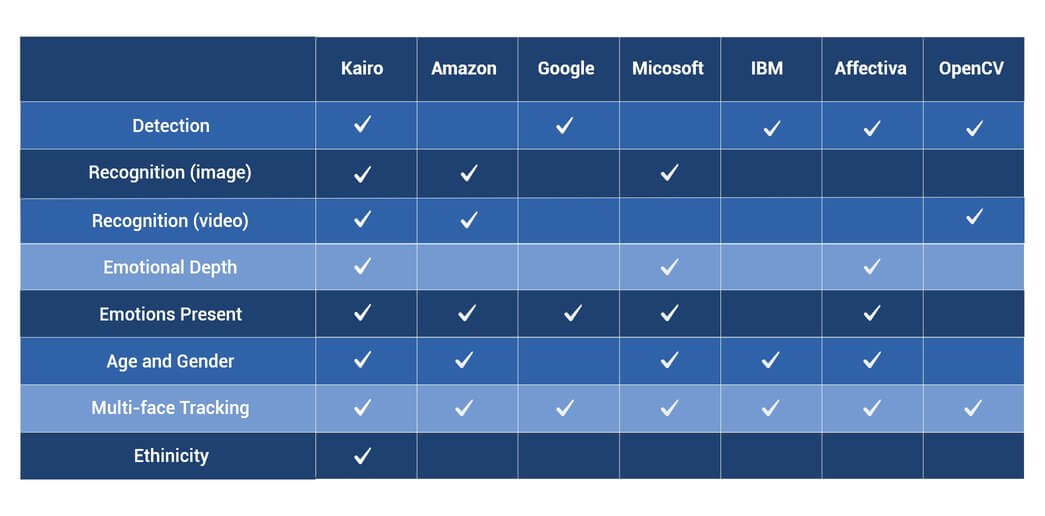
Below is a table to summarise how the API’s discussed above compare.
CONCLUSION
Facial recognition systems are fast becoming part of everyday life due to the simple solutions they furnish to the most essential systems and services. Payment systems are fast adopting the technology to enhance authentication processes, security organizations have already adopted it to gain leverage in the fight against crime, the retail industry has discovered its usefulness in marketing, as the entertainment industry has seen its endless value in creativity.
Unlike the early days of the technology, building applications with facial recognition technologies has never been easier with the advent of cutting edge software development services. Users no longer need to wrestle with the question on how to build the best facial recognition software possible. As Devathon, we have dedicated ourselves to helping you leverage the advantages of facial recognition technology through building apps based on the cutting edge technology. We cherish and enjoy being part of your story as relentless builders of your dream. Drop us an email at hello@devathon.com




Usually I never comment on blogs but your article is so convincing that I never stop myself to say something about it. You’re doing a great job Man, Keep it up.